Puzzles
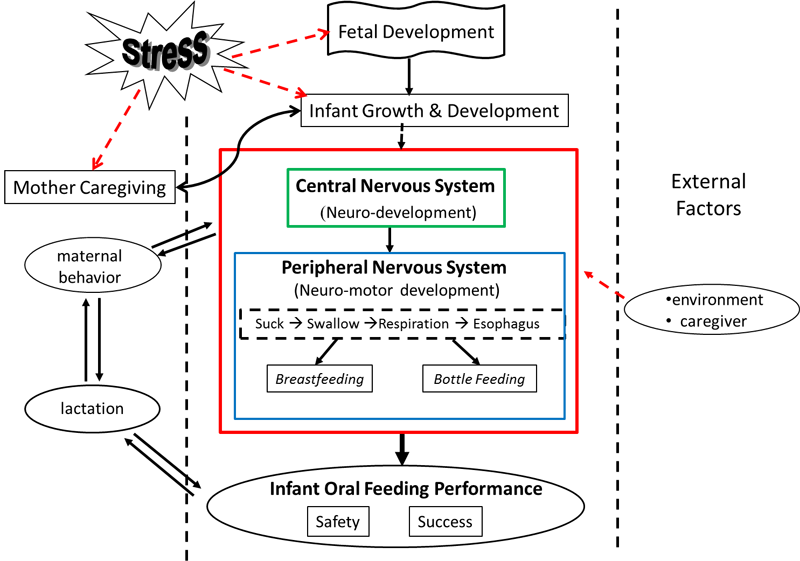
No medical events solely impact on a patient’s condition. This is particularly true with infants who are helpless and must rely on caregivers, specifically their mother, for survival. Consequently, an infant’s growth and development becomes a function, not only on their own maturing attributes and their surroundings, e.g., stress, neonatal intensive care unit or home environment, but also on the quality of their interactions with mother/caregivers during difficult times. If feeding difficulties persist, it is essential that consideration of the quality of interactions within the mother-infant dyad be taken into account.
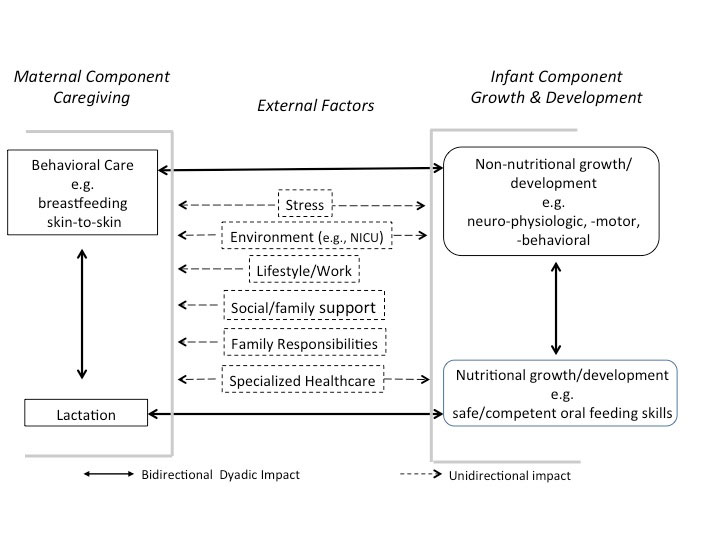
The schematic below describes the intimate relationships of altered maternal and infant "components" that can directly affect infants' oral feeding performance, be they breastfeeding or bottle feeding
Bilateral “give and take” interactions between maternal and infant represent the reciprocal impact that each partner’s action may have on the other, be they beneficial or detrimental (< ---- >); Unilateral arrows have a unidirectional impact on mother and/or infant as they are not controlled by the dyad, be they beneficial or detrimental (----- >)
Mother-Infant Puzzle
Conceptual Model of Breastfeeding Challenges facing Preterm Mother-Infant Dyad - A model presenting four major elements, maternal behavioral and nutritional care and infant non-nutritional and nutritional growth/development, making up the mother-infant dyad with examples of external factors that may impact mother-infant breastfeeding interactions. The bilateral interactions (solid line arrows) between maternal and infant elements represent the reciprocal impact that each partner’s actions may have on the other, be they beneficial or detrimental. The external factors (dashed arrows) have a unidirectional impact on mother and/or infant as they are not controlled by the dyad, be they beneficial or detrimental.